Overview
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is common disease and affects majority of elderly patients. But, it creates symptoms in some and remain silent in rest. It requires treatment in those who have bothersome symptoms affecting quality of life.
Sign & Symptoms
Hesitancy
- Blood in the urine (i.e. hematuria), caused by straining to void
- Dribbling after voiding
- Feeling that the bladder has not emptied completely even after urination
- Frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturia)
- Hesitant, interrupted or weak urine stream caused by decreased force
- Leakage of urine (overflow incontinence)
- Pushing or straining to begin urination
- Recurrent, sudden, urgent need to urinate
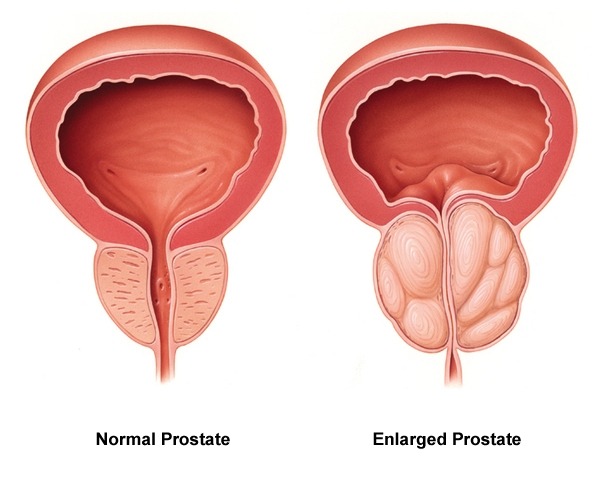
In severe cases of BPH, Acute Urinary Retention (inability to urinate) may result. It causes severe pain and discomfort. Catheterization may be necessary to drain urine from the bladder to obtain relief.
Diagnosis
Clinical symptoms and physical examination provide the basis for diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. The physical examination includes a digital rectal examination (DRE). Symptom evaluation is obtained from the results of the AUA Symptom Index.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
DRE typically takes less than a minute to perform. The doctor inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the patient’s rectum to feel the surface of the prostate gland through the rectal wall to assess its size, shape and consistency. Healthy prostate tissue is soft, like the fleshy tissue of the hand where the thumb joins the palm. Malignant tissue is firm, hard and often asymmetrical or stony like the bridge of the nose. If the examination reveals the presence of unhealthy tissue, additional tests are performed to determine the nature of the abnormality.
AUA Symptom Index
American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index is a questionnaire designed to determine the seriousness of a man’s urinary problems and to help diagnose BPH. The patient answers seven questions related to common symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. How frequently the patient experiences each symptom is rated on a scale of 1 to 5. These numbers added together provide a score that is used to evaluate the condition. An AUA score of 0 to 7 means the condition is mild; 8 to 19, moderate; and 20 to 35, severe.
PSA Test
Blood test to check the levels of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in a patient who may have BPH helps the doctor to eliminate the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Uroflowmetry Test
This is a simple test which records the urine flow to determine how quickly and completely the bladder can be emptied. With a full bladder, the patient urinates into a device that measures the amount of urine, the time taken, and the rate of urine flow. Patients with stress or urge incontinence usually have a normal or increased urinary flow rate, unless there is an obstruction in the urinary tract. A reduced flow rate may indicate BPH.
Post-Void Residual (PVR)
This test measures the amount of urine that remains in the bladder even after urination. The patient is asked to urinate immediately prior to the test and the residual urine is determined by ultrasound. PVR less than 50 ml. generally indicates adequate bladder emptying and measurements of 100 to 200 ml or higher often indicates blockage.
Laser Treatment
Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate (HoLEP):
It is the latest modality used in the management of Enlarged Prostate. In this procedure, a 550 Micron Fibre attached to a 100-Watts Holmium Laser machine is used to remove obstructive prostatic tissue and seal blood vessels. The enucleated gland is then pushed into the bladder, which is later sucked out with the help of an equipment called Morcellator. The whole procedure takes around 45-90 minutes, depending on the size of the gland. This procedure is nearly bloodless as the laser beam when cuts the gland also seals the blood vessels. In most of the cases there is no need for blood transfusion. At the end of surgery, a catheter is inserted to keep the bladder in place. It continuously drains the urine into a sterile collection bag. The catheter is usually kept for 24 to 48 hrs and the patient is discharged without catheter after giving a catheter free trial.
Advantages Of HOLEP Over TURP:
Advantages of Holmium Laser Surgery | |||
OPEN SURGERY | TURP | HOLEP | |
| Prostate Size | Any size | < 120 grams | Any size |
| Catheterization | 5-7 days | 3-5 days | 2 days |
| Blood Transfusion | Usually required | 3-4 in 100 cases | 0-1 in 10,000 patients |
| Bladder Irrigation | Required | Uncommon | Rarely required |
| Hospital Stay | 5-7 days | 3-5 days | 2-3 days |
| Patients with high blood sugar & high blood pressure | High risk | Moderate risk | Minimal risk |
| Patients with poor cardiac status | High risk | Moderate risk | Minimal risk |